What is Proof of Concept?
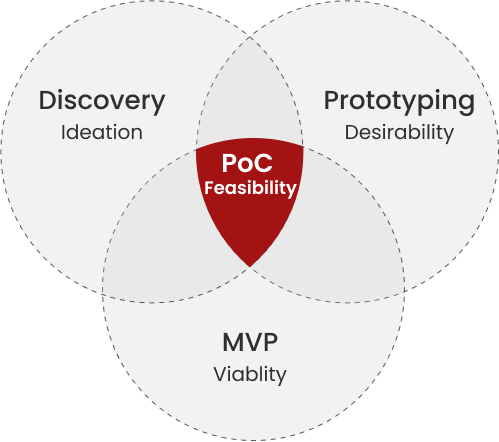
Proof of Concept (PoC) refers to the initial test of an idea, product, or method to determine its feasibility in the market. By completing a proof of concept, businesses essentially determine whether or not an idea can be turned into reality.
Proof of Concept (PoC) takes place after the ideation phase but before design and engineering work, which can also assist businesses with identifying unforeseen risks in the execution or production of the idea.
Proof of concept is a key step before actually prototyping and launching a product.
PoCs can be in the form of a presentation, document, or demo delivered to potential investors, stakeholders, business leaders, and others to illustrate the viability of the concept to gain approval and/or funding.
A PoC report contains information gathered during the testing process, including customer feedback, competitor research, business analysis, financial estimates, and a launch strategy.
What Proof of Concept Does Not Include
Benefits of Doing a PoC
A proof of concept evaluates the feasibility of a concept or plan before development work begins. By verifying concepts and theories developed in the ideation phase, founders improve their odds of delivering a successful final product.
Put Your Vision to the Test with the Help of SaaS Experts
Taking your vision to reality in a responsible and effective way starts with a PoC. Our team of SaaS experts and Solution Architects will collaborate with you to create and refine a detailed proof of concept and mock-ups that can be pitched to investors or internal stakeholders.
The Approach
01
Objective Defining
The proof of concept starts with a consultation – unpacking the current operating environment, resources, tech stack, and what is required to bring the project to fruition.
02
Detailed Planning
Once we understand the objectives and operating environment, we’ll design the development plan in greater detail.
03
Determining Success Criteria
We will determine the criteria for success, the key milestones and objectives, and the capability of the proposed solution in the target market.
Execution Phase
Progress will be tracked and communicated throughout the entire Proof of Concept Phase by the dedicated Account Manager.
Documentation
Once the project has been completed, all of the learnings and justifications will be collected and presented in a detailed PoC report.
Strategic Plan
Once all of the stages are completed and approved, the final plan of execution for the development stage is presented for approval.
How to Decide When You Need a PoC
Only 10% of startups enjoy long-term success. To succeed, businesses need to understand the market, correctly estimate the cost, and solve customer pain points.
By starting your software development process with a Proof of Concept, you are setting your SaaS company up for success from the start. You should complete a Proof of Concept if you want to:
Identify What is Possible
A proof of concept will identify real-life limitations and viable substitutions within the required timeframe by tapping into the expertise of SaaS developers, solution architects, and designers.
Mitigate Risk
Building a new SaaS solution comes with inherent risks. No one wants to build a solution only to discover that they don’t have the resources to complete the project or that their ideas are not technologically viable. A PoC will mitigate many of the risks that new solutions face before development starts.
Gaining Financial Support
Investors require solid evidence that an idea is viable before they will agree to fund it. With a PoC, you can reassure investors of the viability of the concept and demonstrate the expected return on investment to get upper management on your side.
The Team
Project Manager
The PM will coordinate and advise the team, as well as manage risks, resources, and performance. They will also communicate with the client, along with the dedicated Account Manager, to ensure smooth execution.
Business Analyst
Business Analysts are commercial experts that will analyze all aspects of the market and your unique niche. They will outline the issues, suggest solutions, and identify relevant opportunities.
UX/UI Designer
The designer will build intuitive and visually appealing mockups to ensure that the user experience is seamless and goal-orientated.
Systems Architect
The systems architect will examine the entire deployment process and ensure consistent release and continuous integration by building high-availability, redundant environments that can handle any contingency. They will ensure that the key performance metrics are cultivated, communicated and executed. They will also ensure that best practices and operational efficiency is maintained at all times.